# Virtual Event
# I.The Significance of Virtual Events
Combining multiple meta-events and their filtering conditions forms a virtual event, and triggering any meta-event in a virtual event is considered to trigger the virtual event.
Several events with similar meanings can be used to form virtual events, such as the 'core behavior' of the virtual event, which is composed of meta-events of the main behaviors in the product, and can be applied to analysis models such as retention, funnel, etc.
Examples of application scenarios:
- What is the consumer behavior of users who recharge or purchase products in Shanghai?
- Analyze the trend distribution of users who meet the consumption props or use props events.
- Analyze the behavior of users who receive gold coins/diamonds/props rewards from the source channel of Yingyongbao.
# II. Location and Applicable Role of Virtual Events
Click 'Event Management' in 'metadata' to enter the event management list.
| Company Supervisor | Administrator | Analyst | Ordinary members | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| View the list of virtual events | ● | ● | ▲ | ○ |
| Create and edit virtual events | ● | ● | ▲ | ○ |
Permission description:
● Role must have
▲ The role has the permission by default, but can revoke
△ The role is not available by default, but can be authorized
○ Role must not have
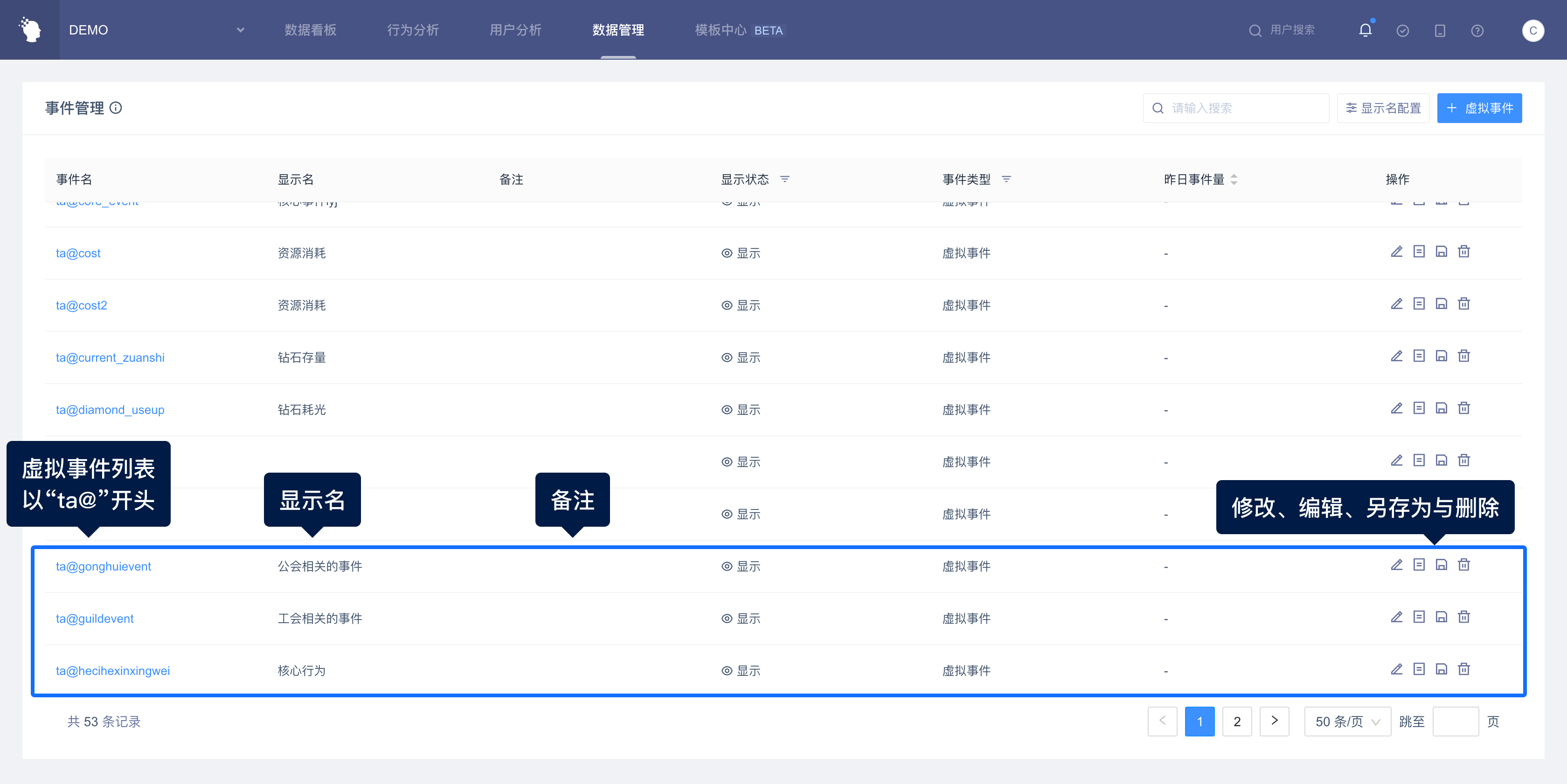
# III. Overview of Virtual Events Page
The virtual event overview diagram is as follows:
# IV. Usage of Virtual Events
# 4.1 Create a Virtual Event
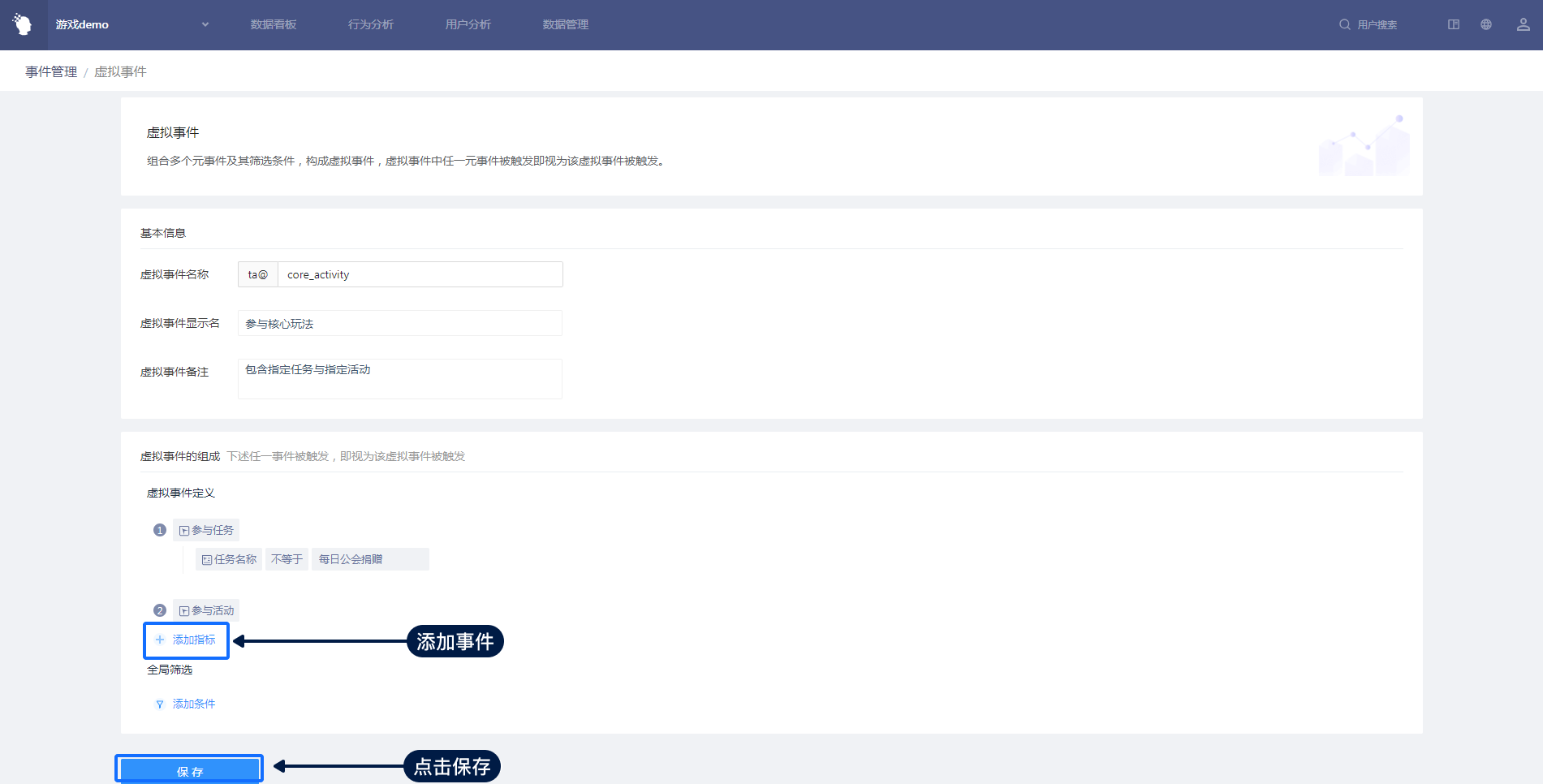
Click '+' to create a virtual event and enter the virtual event editing interface.
# 4.1.1 Precautions
(1) Naming rules: letters can start with letters, numbers and underscores, up to 24 characters.
(2) The relationship between different virtual events belongs to or, and the occurrence of any event shall be regarded as the occurrence of the virtual event.
Take the above screenshot as an example:
- A user completes 1 consumption and 1 use of props, which is equivalent to 2 'prop consumption operations';
- A user completes 1 consumption and 0 use of props, which is equivalent to 1 'prop consumption operation';
- A user completes 0 times to consume props and 1 time to use props, which is equivalent to 1 'prop consumption operation'.
(3) Virtual events follow the principles of union and deduplicate
Take the above screenshot as an example:
User with user_id 00001 consume props and use props on the day of 2019-10-07:
'Prop Consumption' virtual event consists of 'Prop Consumption' meta-event and 'Prop Use' meta-event.
| Event | Number of users triggered | Does it happen | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Consumption props | Use props | ||
| Take virtual events to calculate the number of users triggered by "prop consumption" | 1 | ✅ | ✅ |
| 1 | ✅ | ||
| 1 | ✅ | ||
| Calculate the number of users triggered by two meta-events separately without taking virtual events | 2 | ✅ | ✅ |
| 1 | ✅ | ||
| 1 | ✅ | ||
It can be seen that without taking virtual events, the number of triggered users obtained by directly adding the two events will be repeatedly calculated and deduplicated when taking virtual events.
# 4.1.2 Full Event Filtering
When there is only one meta-event in the virtual event, the 'full event compliance' option does not appear.
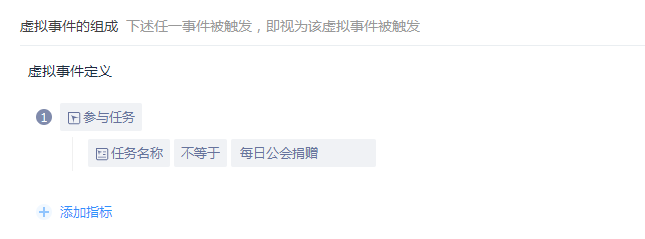
The 'Full Event Compliance' option appears when there are two or more meta events in the virtual event. When the 'Full Event Compliance' filter is created, all meta events occur if the filter is met.
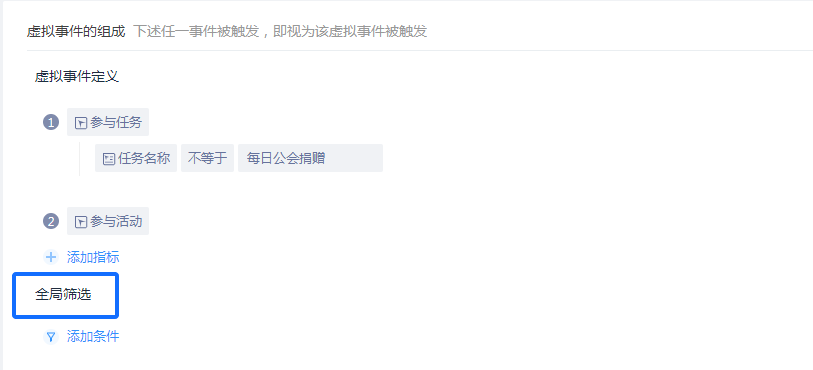
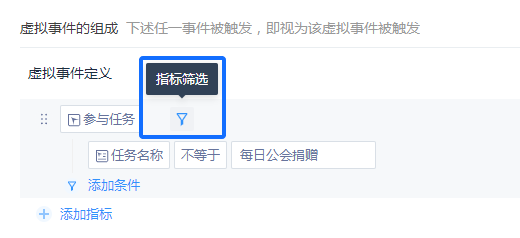
# 4.1.3 Single Event Filtering
This filter can filter an event in a virtual event or all events in a virtual event.
# 4.2 Modify, Edit and Delete Virtual Events
# 4.2.1 Modification
This operation can only modify the display name, display status, comments.

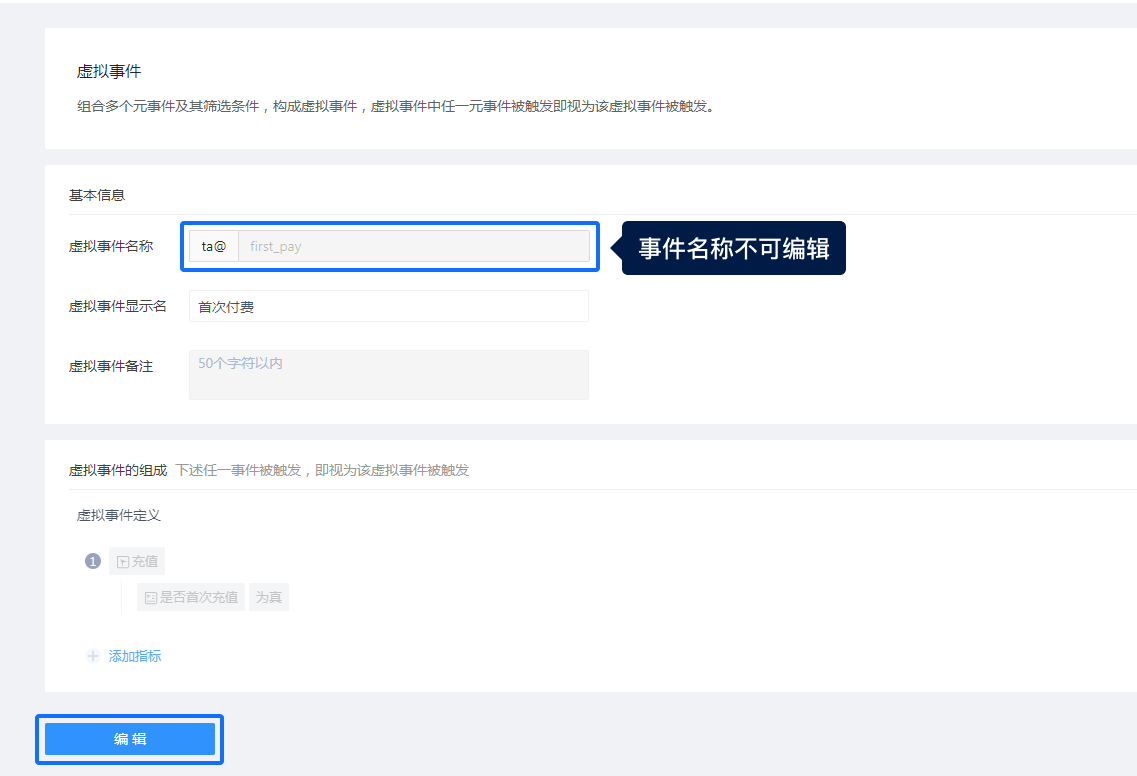
# 4.2.2 Editing
Edit all parts except the virtual event type
You can do this even if you are not the creator of the virtual event.

# 4.2.3 Save As
The operation jumps to the 'Create Virtual Event interface' and replicates the generation logic of the selected virtual event, which you can adjust to generate a new virtual event.

# 4.2.4 Delete
This operation can delete unnecessary virtual events, which cannot be recovered after deletion.

# 4.3 Calculation Rules for Virtual Events
Take the meta-events of some users as an example, and explain them in detail as follows:
Problems to be solved: within the selected date, determine the users who completed the conversion process from 'prop output' to 'prop consumption' on that day.
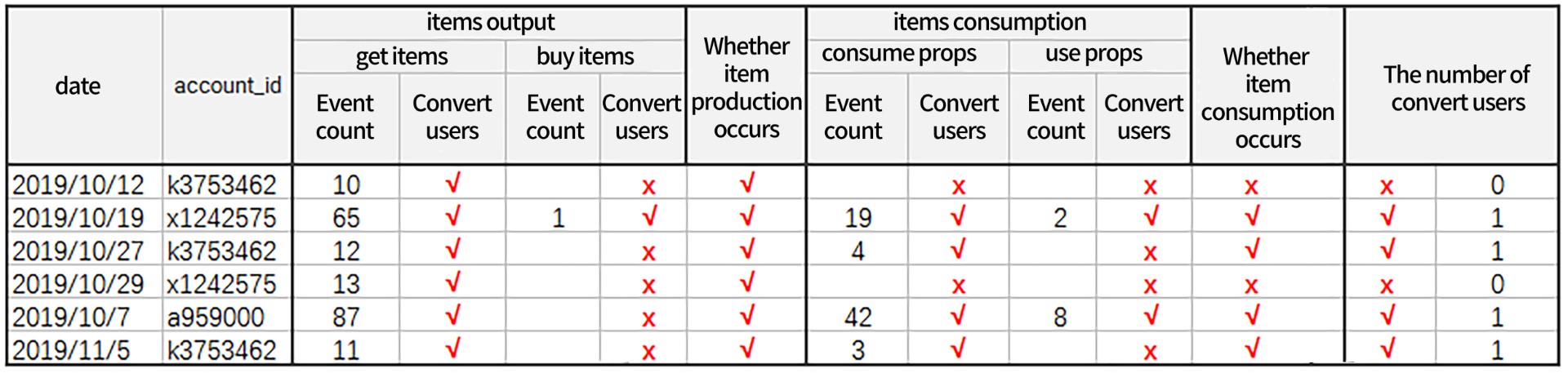
**RESULTS: **According to the following figure, in the selected 6 days, the users who completed the conversion on the same day were x1242575, k3753462, a959000, k3753462, a total of 4.
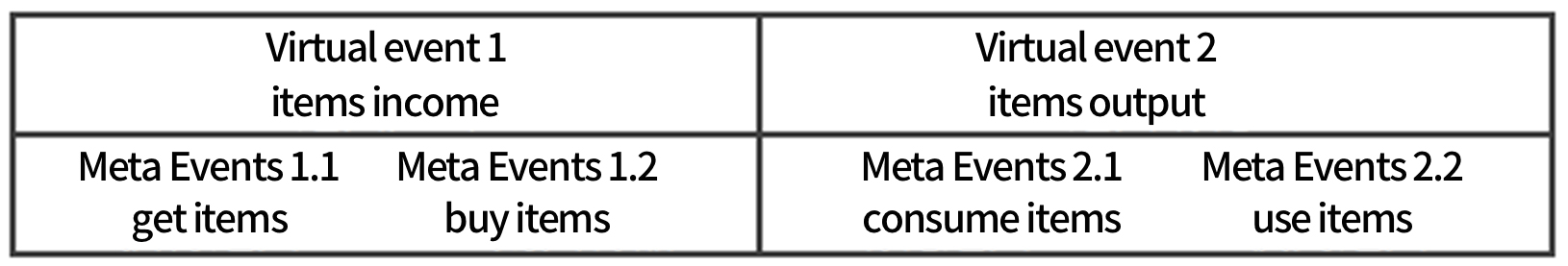
# 4.3.1 Meta Event 1.1 that Only Triggers Virtual Event 1
**For example: **in the above table, only 'obtaining props' under 'props output' occurred on that day
User k3753462 'obtained props' 10 times in 'prop output' on October 12, 2019, which is regarded as 'prop output' behavior; on the same day, 'consumption of props' and 'use of props' did not occur, which means that 'props consumption' behavior did not occur, which means that 'props output' and 'props consumption' did not occur at the same time on the same day.
If it does not conform to the rule of completing the conversion process from 'prop output' to 'prop consumption' on the same day, it will be regarded as 0 conversion users.
# 4.3.2 Meta Events 1.1, 1.2 that Trigger Virtual Event 1 and Meta Events 2.1, 2.2 that Trigger Virtual Event 2
**For example, **in the above table, 'obtaining props' and 'purchasing items' under 'prop output' occurred on the same day, while 'consuming props' and 'using props' under 'prop consumption' occurred at the same time.
On October 19, 2019, user x1242575 'acquired props' 65 times in 'prop output' and 'purchased items' once at the same time, which is regarded as 'prop output' behavior. On the same day, 19 'props were consumed' and 2 'props were used' at the same time, which is regarded as 'props consumption' behavior.
It conforms to the rule of completing the conversion process from 'prop output' to 'prop consumption' on the same day and is regarded as 1 conversion user.
# 4.3.3 Meta Event 1.1 that Triggers Virtual Event 1 and Meta Event 2.1 that Triggers Virtual Event 2
**For example, **in the above table, 'props obtained' under 'props output' and 'props consumed' under 'props consumption' occurred on the same day.
User k3753462 'obtained props' 12 times in 'prop output' on October 27, 2019, and no purchase of items occurred, which is regarded as 'prop output' behavior; 4 times of 'prop consumption' occurred in 'prop consumption' on the same day, and no use of props occurred, which is regarded as 'prop consumption' behavior.
It conforms to the rule of completing the conversion process from 'prop output' to 'prop consumption' on the same day and is regarded as 1 conversion user.
# V. Best Applications
# 5.1 Merge Similar Data
During data collection, multiple events may be logically related. For example, prop output may be recorded in events such as 'obtain props', 'purchase props' and 'monster falling'. Prop consumption may be recorded in events such as 'consuming props', 'using props' and 'expiring props'. In this case, if you want to analyze the output and consumption of props, you can use virtual events to merge similar data and use virtual events in analysis.
# 5.2 Convert Common Event and Filter Condition Groups
In some cases, some events often use the same filtering condition when they are used. For example, if you want to analyze home page browsing, you will analyze the filtering of 'page browsing' events plus 'web page equals home page', or the first-time payment event, you will use 'paid event' plus 'whether it is true for the first time'. In these cases, you can convert the combination of such events and filter conditions into virtual events, and this event can be selected directly during analysis without having to add filters again, making it easier to operate.
