# Entities
# What are entities?
Entity analysis means identifying and analyzing the unique users based on such dimensions as device ID, account ID, role ID, and platform ID. TE user ID is the preset user entity. You could also create self-defined user entities based on existing event properties or user properties and use such user entities in future retention analysis, funnel analysis, distribution analysis, interval analysis, or tag cohort.
# Set User Entities
Select「project settings」on the right corner of the page and enter Settings > Entity menu.
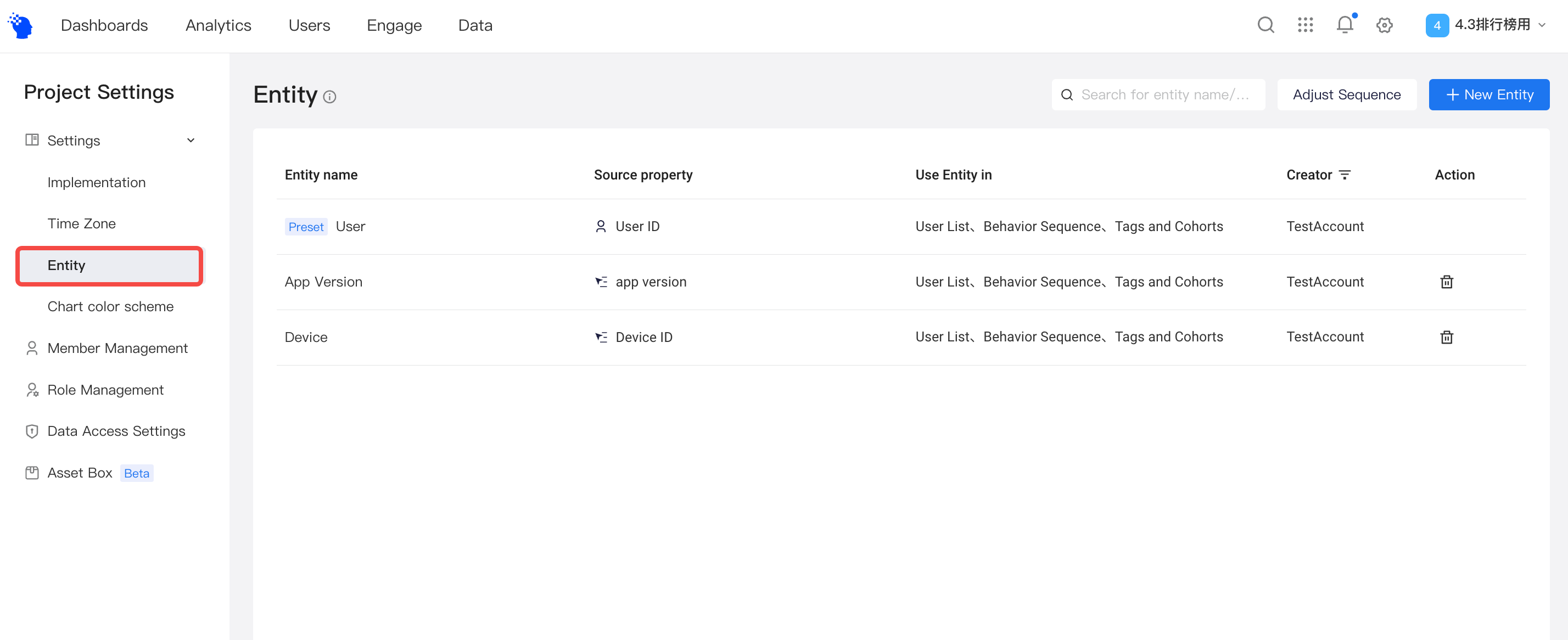
- The preset user entities (TE user ID), configured by default, could not be deleted. However, the name of preset user entities could be modified.
- You have to configure self-defined user entities by yourself. If you have configured「user identification system」in v3.3 or earlier versions, you can find the user entities you defined in the list of self-defined user entities.
| Root admin | Administrator | Analyzer | Ordinary members | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Configure user entities | ● | ● | ○ | ○ |
| Use user entities | ● | ● | ● | ○ |
Instruction on permissions:
● The role must have the permission.
▲The role should have the permission by default. It is also acceptable for the role to have no such permission.
△ The role should not have the permission by default. It is also acceptable for the role to have such permission.
○ The role must not have the permission
# Create new entities
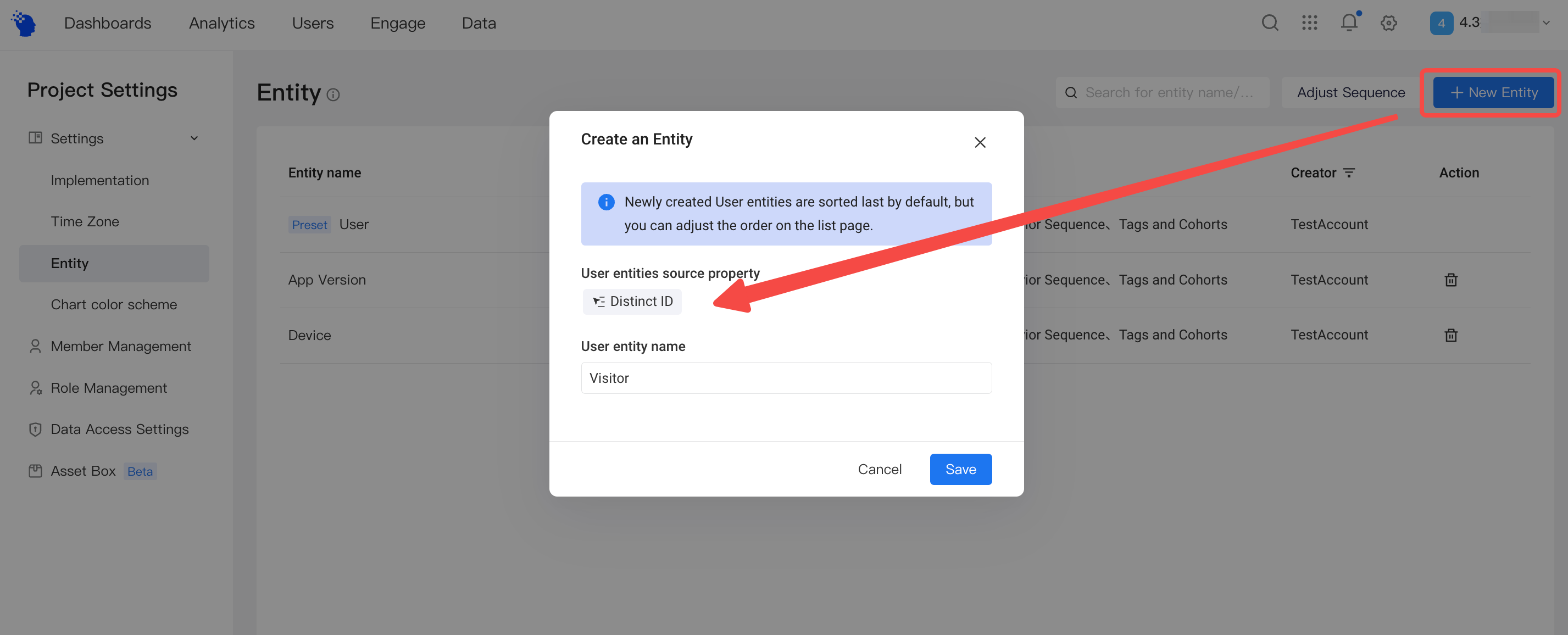
Enter project settingst>entities, click「add new entity」, and fill out the name and source of entities.
# Adjust entities orders
By default, entities are displayed in the order of: the preset entity, custom entities, with all the custom entities ordered by their creation time. This order is also the order for display when using entities in analysis. If you need to adjust the orders and make the most frequently used entity the first option, you can re-order the entities through 'Adjust Sequence' on the top right of the page. You may drag the entity to their desired place in the sequence, or simply 'pin' a entity to make it the top of the sequence.
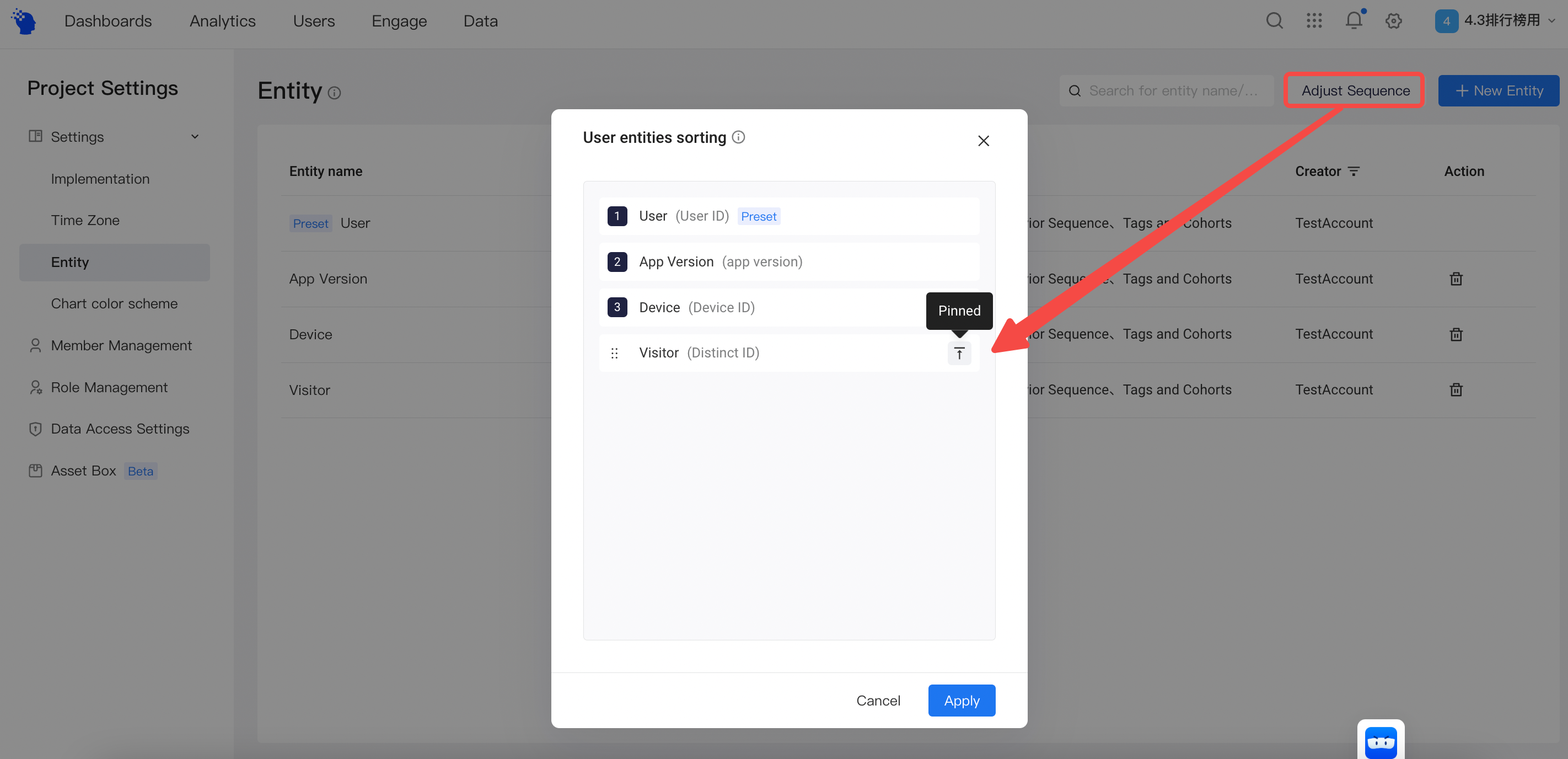
Once the adjustments are applied, you can find the entity list when creating new reports, new tags, new cohorts using the new sequence. Please note that when using entities in analysis, ones that are irrelevant to the current metrics are filtered and will not display.
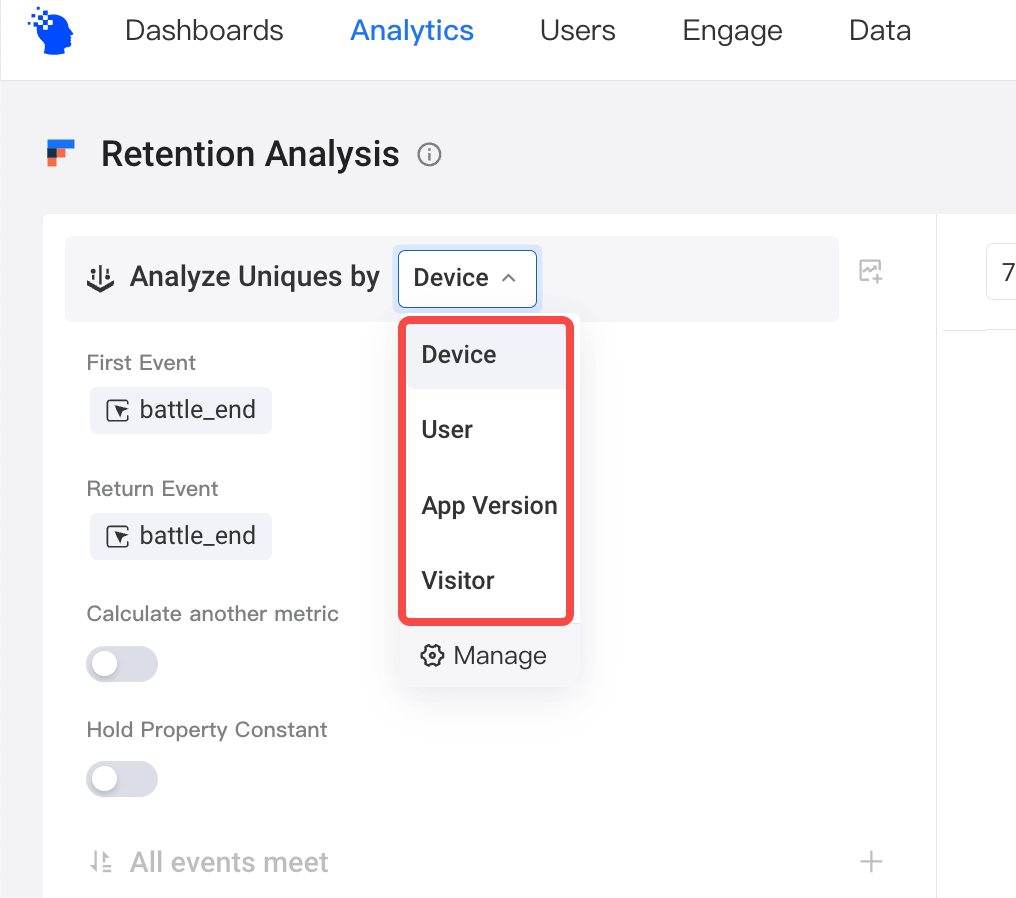
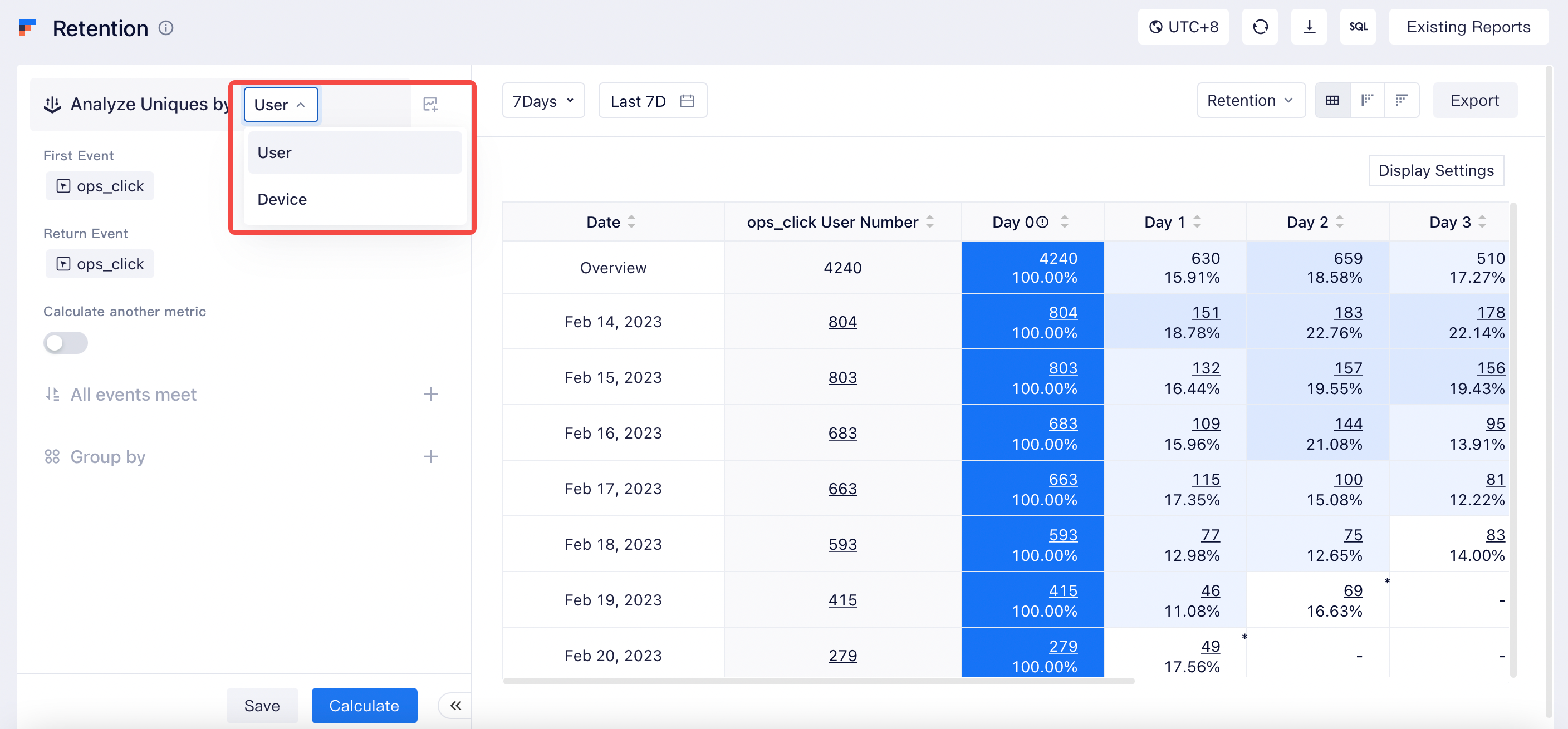
# Use in analysis models
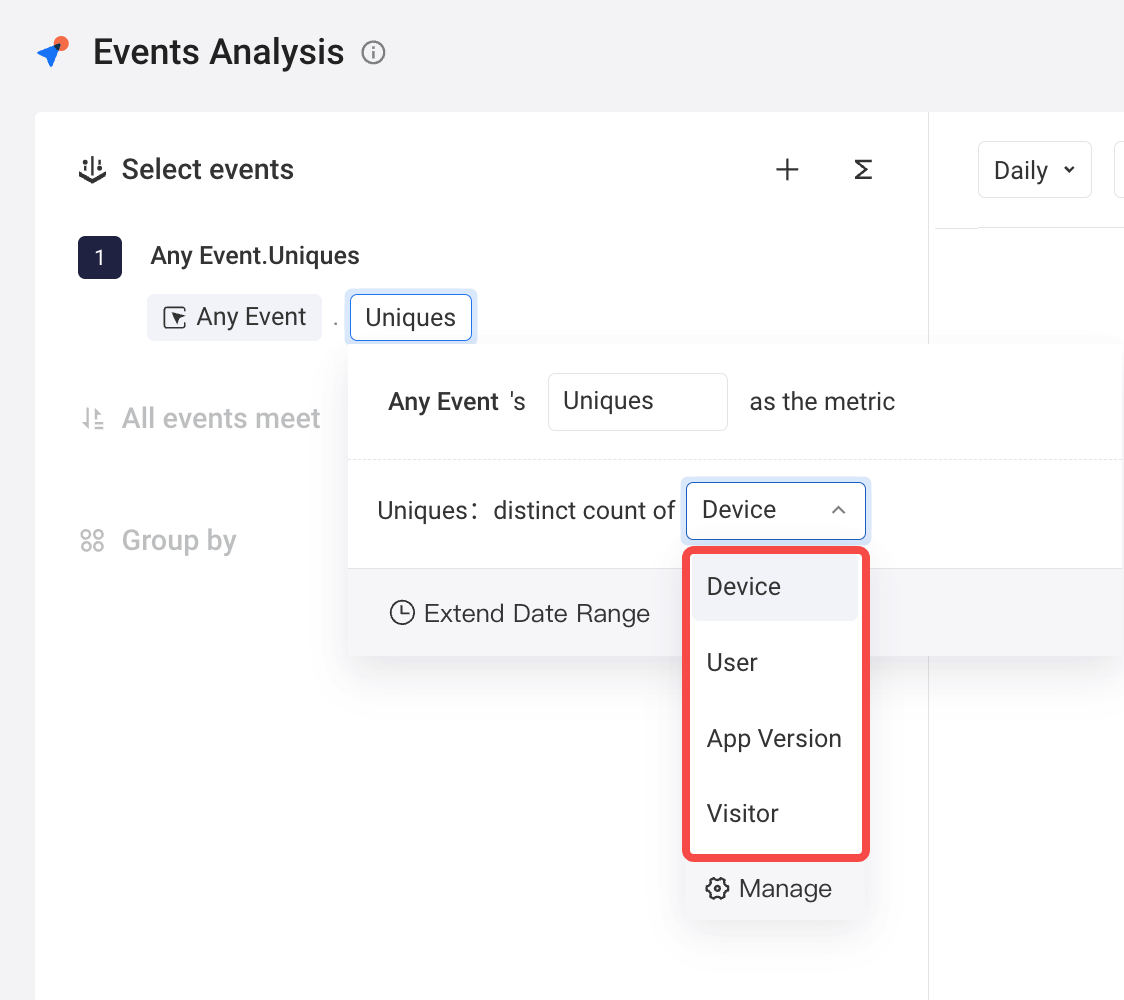
Currently, user entity switching is supported by four analysis models, including retention analysis, funnel analysis, distribution analysis, and interval analysis. You can click the upper left corner to check the configured user entities. Preset user entities are used by default.
# Use in cohorts/tags
A user entity should be selected from the configured user entities to help create cohorts or tags, based on which the cohorts/tags would perform computation based on the selected user entity and definition. For more information about creating self-defined cohorts/tags, please refer to the user cohorts and user tags 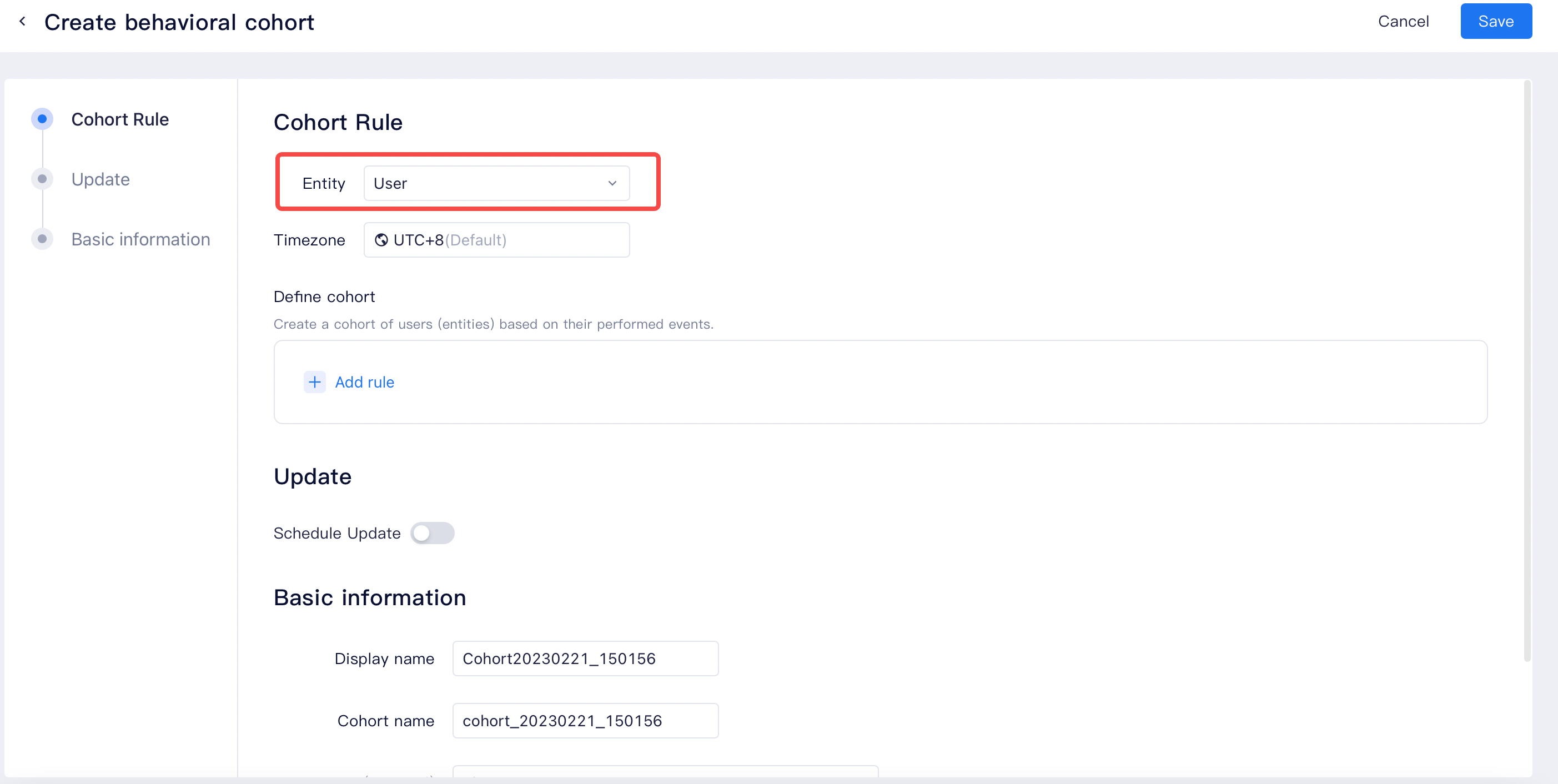
# Use Cases of User Entities
# Use entities in retention analysis
- The retention/loss of each role dimension after the same user uses multiple game roles for a certain period.
- The retention/loss of core behaviors of role dimensions when the user is fighting
- Since a user may log in with multiple devices, analyze LTV performance from the device dimension.
# Use entities in funnel analysis
- Analyze rank transformation within a certain period from the perspective of the role.
- Analyze the process from starting the fight to winning the fight within a certain period from the perspective of the role.
- Analyze new user charging within a certain period of time from the perspective of the device.
# Use entities in distribution analysis
- Rank residing of the role dimension
- User activeness of the device dimension
- Player charging distribution of the role dimension
# Best Practice
# Use custom entities in models
According to the computational logic of the retention, funnel, distribution, and interval model, contextual computing could only be performed based on the source property of user entities. For instance, when the distribution analysis model checks the distribution of the login days of users, the results based on roles would be different from those based on accounts. If an account has multiple roles, login of any of the roles would be included in the computation.
# Analyze the organizational structure dimensions of users
Under certain conditions, users might be located in certain organizational structures, namely, guilds in games, stores in E-commerce, and teachers of training APPs. Analysis of these dimensions could also take these properties could also be used as the source of self-defined user entities and switch to such user entities For example, in distribution analysis, if the user entity is switched to "guild" to analyze the amount paid, the results would be the sum and distribution of the amount paid for all roles under the guild.
